Unlocking the Potential of Edge Computing in IoT
The digital milieu is swiftly metamorphosing, with the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing pioneering this revolution. Edge computing in IoT is a seminal advancement, offering unparalleled benefits and sculpting the future of technology. This disquisition delves into the benefits of edge computing, its application in IoT, and the future of edge computing technology.
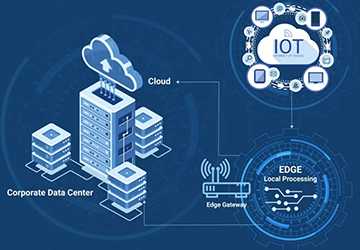
The Fundamentals of Edge Computing
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing epitomizes a decentralized data processing paradigm where computation transpires proximate to the data source rather than in a centralized cloud environment. This proximity to the data source augments the efficiency and celerity of data processing, rendering it highly appropriate for IoT applications.
The Role of IoT in Contemporary Technology
The Internet of Things (IoT) denotes the interconnected panoply of devices communicating and sharing data. The amalgamation of edge computing in IoT permits these devices to process data in situ, mitigating latency and ameliorating real-time decision-making.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Enhanced Performance
A quintessential benefit of edge computing is augmented performance. By processing data at the edge, near its point of origin, the temporal interval requisite for transmitting data to and from the central server is markedly diminished.
Reduced Latency
Edge computing significantly abates latency, which is paramount for applications necessitating instantaneous responses, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Improved Security
With edge computing in IoT, sensitive data can be processed locally, thus attenuating the risk of data breaches during transmission. This local processing confers an additional stratum of security, particularly advantageous for critical applications.
Cost Efficiency
Another salient benefit of edge computing is cost efficiency. By diminishing the quantum of data that must be transmitted to the cloud, organizations can economize on bandwidth expenditures and alleviate the load on central servers.
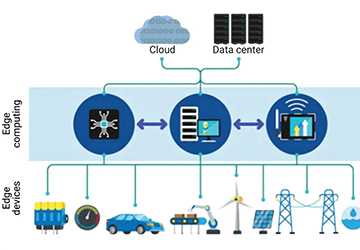
Edge Computing in IoT Applications
Smart Cities
In smart cities, edge computing in IoT is instrumental in managing resources efficaciously. For instance, intelligent traffic systems can process data locally to optimize traffic flow and alleviate congestion.
Healthcare
In the healthcare domain, edge computing in IoT is revolutionizing patient care. Wearable devices can monitor patient vitals in real time and process data locally to provide immediate alerts to healthcare providers in the event of anomalies.
Industrial Automation
Industrial IoT applications reap substantial benefits from edge computing. By processing data at the edge, factories can monitor and control machinery in real-time, enhancing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Retail
In the retail sector, edge computing in IoT augments customer experience through personalized services. For example, intelligent shelves can monitor inventory in real-time and process data to ensure timely restocking.
Future of Edge Computing Technology
Growing Adoption
The future of edge computing technology appears promising, with escalating adoption across diverse industries. As more devices become interconnected, the demand for edge computing solutions will continue to burgeon.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with edge computing in IoT will further amplify its capabilities. These technologies can analyze data locally, rendering predictive analytics and real-time decision-making more efficacious.
Enhanced Connectivity
The future of edge computing technology will witness enhanced connectivity with the advent of 5G networks. This high-velocity connectivity will enable expedited data processing and lower latency, making edge computing more efficient.
Sustainability
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a critical consideration in technological development. Edge computing contributes to sustainability by reducing the energy consumption associated with data transfer to and from central servers.
Challenges and Solutions
Data Management
Managing voluminous data at the edge can be challenging. However, advancements in storage solutions and data management techniques are addressing these challenges, making edge computing in IoT more feasible.
Standardization
The need for more standardization in edge computing technology presents a problem. Developing industry-wide standards will be crucial for seamless integration and interoperability of edge computing solutions.
Security Concerns
While edge computing enhances security by processing data locally, it introduces novel security challenges. Implementing robust security measures at the edge will be essential to safeguard against potential threats.
Innovations in Edge Computing
Distributed Intelligence
The amalgamation of edge computing in IoT has engendered the concept of distributed intelligence, wherein data processing faculties are disseminated across variegated nodes. This empowers IoT devices to engage in autonomous decision-making, augmenting operational efficacy and alacrity.
Data Sovereignty
One of the emergent benefits of edge computing is the facilitation of data sovereignty. Organizations can more effectively comply with regional data protection statutes by localizing data processing, ensuring that sensitive information remains within specified geographical confines.
Fault Tolerance
Edge computing in IoT fortifies fault tolerance by decentralizing data processing. This paradigm ensures that even if one node succumbs to malfunction, other nodes can perpetuate operations, thereby providing resilience and uninterrupted service.
Emerging Trends in Edge Computing Technology
Federated Learning
Federated learning is an innovative methodology in which edge computing in IoT devices collaboratively trains machine learning models while maintaining data localization. This technique enhances privacy and reduces data transfer costs, making it ideal for sensitive applications.
Edge-AI Synergy
The confluence between edge computing and artificial intelligence (AI) engenders new possibilities. By embedding AI capabilities at the edge, devices can perform intricate analyses and make autonomous decisions without reliance on centralized cloud resources.
Micro Data Centers
The deployment of micro data centres is an ascendant trend in the future of edge computing technology. These miniature data centres near the source provide formidable computing power and storage, ensuring low latency and high performance.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
Data Governance
Effective data governance policies will be paramount in the epoch of edge computing in IoT. Organizations must institute robust frameworks to manage data ownership, privacy, and compliance, ensuring data is utilized ethically and responsibly.
Security Standards
Stringent security standards must be developed and adhered to to safeguard edge computing technology; this entails implementing encryption, access controls, and regular audits to protect against cyber threats and ensure data integrity.
Investment and Funding
Strategic investments and funding will shape the future of edge computing technology. Governments and private entities must allocate resources to research and development, fostering innovation and accelerating the adoption of edge computing solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, edge computing's benefits are manifold, and its integration with IoT is transforming diverse industries. The future of edge computing technology is luminous, with advancements in AI, ML, and connectivity promising to unlock even more significant potential. As we forge ahead, overcoming the challenges associated with edge computing will be pivotal in fully realizing its benefits.